Abstract
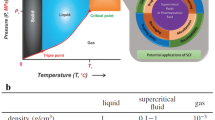
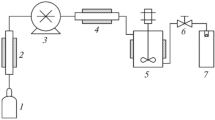
The application of supercritical fluid (SF) processing in pharmaceutical research is increasing particularly in the field of particle formation for drug delivery systems. The SF processes have benefits over the existing particle formation methods in terms of improved control, flexibility and operational ease. This review highlights the fundamental concepts of fluid phase behaviour and their influence on the various processes involving particle formation with supercritical fluids. Several phase behaviour systems are discussed to provide an insight into the factors influencing the process paths and their effects on the characteristics of the particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M. A. McHugh and V. J. Krukonis. Supercritical Fluid Extraction. Principles and Practice 2nd Edition, Butterworth-Heinemann, USA, 1994.
S. Angus, B. Armstrong, and K. De Reuk. International thermodynamic tables of the fluid state-3. Carbon dioxide (Volume 3). Pergamon Press, 1976.
K. Stephan and K. Lucas. Viscosity of dense fluids. Plenum Press, New York, 1979.
J. M. Dobbs, J. M. Wong, and K. P. Lohnston. Nonpolar cosolvents for solubility enhancement in supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 31:303–308 (1986).
J. M. Dobbs, J. M. Wong, R. J. Lahiere, and K. P. Johnston. Modification of supercritical fluid phase behaviour using polar cosolvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 26:56–65 (1987).
J. G. Van Alsten and C. A. Eckert. Effect of entrainers and of solute size and polarity in supercritical fluid solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 38:605–610 (1993).
P. Alessi, A. Cortessi, I. Kikic, N. R. Foster, S. J. Macnaughton, and I. Combo. Particle production of steroid drugs using supercritical fluid processing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 35:4718–4726 (1996).
S. S. T. Ting, S. J. Macnaughtn, D. L. Tomasko, and N. R. Foster. Solubility of naproxen in supercritical carbon dioxide with and without cosolvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 32:1471–1481 (1993).
Z. Knez, M. Skerget, P. Sencar-Bozic, and A. Rizner. Solubility of nifedipine and nitrendipine in supercritical CO2. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 40:216–220 (1995).
B. Subramaniam, R. A. Rajewski, and K. Snavely. Pharmaceutical processing with supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Pharm. Sci. 86:885–890 (1997).
I. Kikic and P. Sist. Applications of supercritical fluids to pharmaceuticals: Controlled drug release systems. 2 nd NATO ASI on Supercritical Fluids, Kemer, Turkey. 1998.
H. Tanaka and M. Kato. Vapour-liquid equilibrium properties of carbon dioxide+ethanol mixture at high pressures. J. Chem Eng. Jap. 28:263–266 (1995).
K. Suzuki, H. Sue, M. Itou, R. L. Smith, H. Inlmata, K. Arai, and S. Saito. Isothermal vapour-liquid equilibrium data for binary systems at high pressures: Carbon dioxide-methanol, carbon dioxide-ethanol, carbon dioxide-1-propanol, methane-ethanol, methane-1-propanol, ethane-ethanol and ethane-1-propanol systems. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 35:63–66 (1990).
DECHEMA Chemistry Data Series, 1981.
S. Ohe. Vapour-liquid equilibrium data at high pressure. Elsevier, Japan. 1990.
R. E. Fornari, P. Alessi, and I. Kikic. High pressure fluid phase equilibria: Experimental methods and systems investigated (1978–1987). Fluid Phase Equilibria. 57:1–33 (1990).
R. Dohrn and G. Brunner. High-pressure fluid phase equilibria: Experimental methods and systems investigated (1988–1993). Fluid Phase Equilibria. 106:213–282 (1995).
M. L. Gilbert and M. E. Paulaitis. Gas-liquid equilibrium for ethanol-water-carbon dioxide mixtures at elevated pressures. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 31:296–298 (1986).
S. Yao, Y. Guan, and Z. Zhu. Investigation of phase equilibrium for ternary systems containing ethanol, water and carbon dioxide at elevated pressures. Fluid Phase Equilibria. 99:249–259 (1994).
G. Brunner. Gas Extraction: An introduction to fundamentals of supercritical fluids and the application to separation processes. Springer, New York, 1994.
R. G. Wissinger and M. E. Paulaitis. Glass transtions in polymer/CO2 mixtures at elevated pressures. J. Pol. Sci. B. 29:631–633 (1991).
D. W. Matson, R. C. Peterson, and R. D. Smith. Production of fine powders by the rapid expansion of supercritical fluid solutions. Adv. In Ceramics. 21:109 (1987).
J. W. Tom and P. G. Debenedetti. Particle formation with supercritical fluids-A Review. J. Aerosol. Sci. 22:555–584 (1991).
E. M. Philips and V. J. Stella. Rapid expansion from supercritical solutions: application to pharmaceutical processes. Int. J. Pharm. 94:1–10 (1993).
B. L. Knutson, P. G. Debenedetti, and J. W. Tom. In S. Cohen, H. Bernstein (eds.), Microparticulate systems for the delivery of proteins and vaccines, Drugs and the Pharmaceutical Sciences Series, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, 1996, 77, 89–125.
D. W. Matson, K. A. Norton, and R. D. Smith. Making powders and films from supercritical solutions. CHEMTECH, 8:480–486 (1989).
A. K. Lele and A. D. Shine. Morphology of polymers precipitated from a supercritical solvent. AIChE J. 38:742–752 (1992).
C. J. Chang and A. D. Randolph. Precipitation of microsize organic particles from supercritical fluids. AIChE J. 35:1876–1882 (1989).
D. W. Matson, C. R. Petersen, and R. D. Smith. Production of powders and films by the Rapid Expansion of Supercritical Solutions. J. Mat. Sci. 22:1919–1928 (1987).
J. W. Tom, G. Lim, P. G. Debenedetti, and R. K. Prud'homme. Applications of supercritical fluids in the controlled release of drugs. ACS Symp. Series. 514:238–257 (1993).
J. W. Tom and P. G. Debenedetti. Precipitation of poly(L-lactic acid) and composite poly(L-lactic acid)-pyrene particles by rapid expansion of supercritical solutions. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 7:9–29 (1994).
J. H. Kim, T. E. Paxton, and D. L. Tomasko. Microencapsulation of naproxen using Rapid Expansion of Supercritical Solutions. Biotechnol Prog. 12:650–661 (1996).
A. Kordikowski, A. P. Schenk, R. M. Van Nielen and C. J. Peters. Volume expansions and vapour-liquid equilibria of binary mixtures of a variety of polar solvents and certain near-critical solvents. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 8:205–216 (1995).
E. Reverchon. Supercritical antisolvent precipitation: Its application to microparticle generation and products fractionation. In Proceedings of the 5 th Meeting on Supercritical Fluids. Materials and Natural products processing. Nice, France, 1998, Tome 1, pp. 221–236.
L. Benedetti, A. Bertucco, and P. Pallado. Production of micronic particles of biocompatible polymer using supercritical carbon dioxide. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 53:232–237 (1997).
A. Bertucco, P. Pallado, and L. Benedetti. Formation of biocompatible polymer polymer microspheres for controlled drug delivery by a supercritical antisolvent technique. In Ph. R. Von Rohr and Ch. Trepp (eds.), Process Technology Procedings, 12, High Pressure Chemical Engineering, Elsevier, Netherlands, 1996, pp. 217–222.
F. E. Wubbolts, C. Kersch, and V. Rosmalen. Semi-batch precipitation of acetaminophen from ethanol with liquid carbon dioxide at a constant pressure. In Proceedings of the 5 th Meeting on Supercritical Fluids. Materials and natural products processing. Nice, France, 1998, Tome 1, pp. 249–256.
D. J. Dixon, K. P. Johnston, and R. A. Bodmeier. Polymeric materials formed by precipitation with a compressed fluid antisolvent. AIChE J. 39:127–139 (1993).
E. Kiran and W. Zhuang. Miscibility and phase separation of polymers in near-and supercritical fluids. ACS Symposium Series. 670:2–36 (1997).
S. D. Yeo, G. Lim, P. G. Debenedetti, and H. Bernstein. Formation of microparticulate protein powders using a supercritical fluid antisolvent. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 41:341–346 (1993).
P. R. Sassiat, P. Mourier, M. H. Caude, and R. H. Rosset. Measurement of diffusion coefficients in supercritical carbon dioxide and correlation with the equation of Wilke and Chang. Anal. Chem. 59:1164–1170 (1987).
T. W. Randolph, A. D. Randolph, M. Mebes, and S. Yeung. Sub micrometer sized biodegradable particles of poly(L-lactic acid) via the gas antisolvent spray precipitation process. Biotechnol. Progr. 9:429–435 (1993).
S. Mawson, S. Kanakia, and K. P. Johnston. Coaxial nozzle for control of particle morphology in precipitation with a compressed fluid antisolvent. J. Appl. Pol. Sci. 64:2105–2118 (1997).
R. E. Treybal. Mass transfer operations. McGraw Hill, USA, 1980.
M. Hanna and P. York. Method and apparatus for the formation of particles. Patent No: PCT/GB94/01426. 1994.
M. Hanna and P. York. Particle engineering by supercritical fluid technologies for powder inhalation drug delivery. In Proceedings of Respiratory Drug Delivery V, Pheonix, USA, 1996, pp. 231–239.
M. Hanna, P. York, and B. Y. Shekunov. Control of the polymorphic forms of a drug substance by solution enhanced dispersion by supercritical fluids (SEDS). In Proceedings of the 5 th Meeting on Supercritical Fluids. Materials and natural products processing. Nice, France, 1998, Tome 1, pp. 325–330.
S. Jaarmo, M. Rantakyla, and O. Aaltonen. Particle tailoring with supercritical fluids: Production of amorphous pharmaceutical particles. In Proceedings of the 4 th International Symposium on Supercritical Fluids, Sendai, Japan, 1997, pp. 263–266.
S. Palakodaty, M. Hanna, P. York, D. Rudd, and J. Pritchard. Particle formation using Supercritical fluids—A novel approach. In Proc. 1997 ICheME Event, UK. ISBN: 0 85295 389 5, 1:501–504 (1997).
M. Hanna and P. York. Method and apparatus for the formation of particles. Patent No.: PCT/GB95/01523. 1995.
R. Sloan, M. E. Hollowood, W. Ashraf, P. York, and G. O. Humphreys. Supercritical fluid processing: Preparation of stable protein particles. In Proceedings of the 5 th Meeting on Supercritical Fluids. Materials and natural products processing. Nice, France, 1998, Tome 1, pp. 301–306.
S. Palakodaty, J. Pritchard, P. York, and M. Hanna. Crystallisation of lactose using solution enhanced dispersion by supercritical fluid (SEDS) technique. In Proceedings of the 5 th Meeting on Supercritical Fluids. Materials and natural products processing. Nice, France, 1998, Tome 1, pp. 275–280.
Palakodaty, P. York, and J. Pritchard. Supercritical fluid processing of materials from aqueous solutions: The application of SEDS to lactose as a model substance. Pharm. Res. In press. (1998).
E. Weidner, R. Steiner, and Z. Knez. Powder generation from polyethyleneglycols with compressible fluids. In Ph. R. Von Rohr and Ch. Trepp (eds.), Process Technology Procedings 12, High Pressure Chemical Engineering, Elsevier, Netherlands, 1996, pp. 223–228.
S. Srcic, P. Sencar-Bozic, Z. Knez, and J. Kerc. Improvement of nifedipine dissolution characteristics using supercritical CO2. Proceedings of the 16 th Pharmaceutical Technology Conference and Exhibition, Athens, Greece. 1997, pp. 59–69.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palakodaty, S., York, P. Phase Behavioral Effects on Particle Formation Processes Using Supercritical Fluids. Pharm Res 16, 976–985 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011957512347
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011957512347