Abstract
Purpose. To delineate the contributions of electrorepulsion and electroosmosis to the iontophoretic flux of 5-FU across porcine skin in vitro. Also, the isoelectric point (pI) of the skin model was determined.
Methods. The electrotransport of 5-FU, anode-to-cathode ('anodal') and cathode-to-anode ('cathodal') was determined as a function of the pH of the electrolyte bathing the skin.
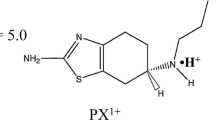
Results. At pH 8.5, the drug (pKa ∼8) is negatively charged and 'cathodal', viz. electrorepulsive, transport is much greater than that in the opposite direction. At pH 7.4, where ∼25% of 5-FU is charged, electrorepulsive and electroosmotic ('anodal') fluxes are balanced. Decreasing the pH to 6, and then 5, reduces the percentage of ionized 5-FU such that 'anodal' electroosmosis dominates across the negatively-charged membrane. But, at pH 4, 'anodal' and 'cathodal' fluxes are again equal suggesting neutralization of the skin (i.e., pI ∼ 4). This is confirmed at pH 3, where 'cathodal' electroosmosis dominates across the now net-positively charged barrier.
Conclusions. Electrotransport is sensitive, mechanistically, to the properties of the permeant and of the skin; interactions of, for example, the drug or constituents of a formulation, that alter the barrier's net charge, can affect iontophoretic delivery. The pI of porcine ear skin is ∼4.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
R. R. Burnette and B. Ongpipattanakul. Characterization of the permselective properties of excised human skin during iontophoresis. J. Pharm. Sci., 76:765-773 (1987).
A. Kim, P. G. Green, G. Rao, and R. H. Guy. Convective solvent flow across the skin during iontophoresis. Pharm. Res., 10:1315-1320 (1993).
M. J. Pikal. Transport mechanisms in iontophoresis. I. A theoretical model for the effect of electroosmotic flow on flux enhancement in transdermal iontophoresis. Pharm. Res., 7:118-126 (1990).
M. J. Pikal and S. Shah. Transport mechanisms in iontophoresis. II. Electroosmotic flow and transference number measurements for hairless mouse skin. Pharm. Res., 7:213-221 (1990).
P. G. Green, R. S. Hinz, C. Cullander, G. Yamane, and R. H. Guy. Iontophoretic delivery of amino acids and amino acid derivatives across the skin In vitro. Pharm. Res., 8:1113-1120 (1991).
N. G. Turner, L. Ferry, M. Price, C. Cullander, and R. H. Guy. Iontophoresis of poly-L-lysines: the role of molecular weight? Pharm. Res., 14:1322-1331 (1997).
M. S. Roberts, P. M. Lai, S. E. Cross, and N. H. Yoshida. Solute structure as a determinant of iontophoretic transport. In R. O. Potts, R. H. Guy (eds.). Mechanisms of Transdermal Delivery, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1997, pp. 291-349.
P. Glikfeld, C. Cullander, R. S. Hinz, and R. H. Guy. A new system for in vitro studies of iontophoresis. Pharm. Res., 5:443-446 (1988).
B. C. Rudy and B. Z. Senkowski. In K. Florey (ed.). Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances, Academic Press, New York, 1973, Vol. 2:221-244.
A. Luzardo-Alvarez, M. Rodríguez-Fernández, J. Blanco-Méndez, R. H. Guy, and M. B. Delgado-Charro. Iontophoretic permselectivity of mammalian skin: characterization of hairless mouse and porcine membrane models. Pharm. Res., 15:984-987 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merino, V., López, A., Kalia, Y.N. et al. Electrorepulsion Versus Electroosmosis: Effect of pH on the lontophoretic Flux of 5-Fluorouracil. Pharm Res 16, 758–761 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018841111922
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018841111922