Abstract
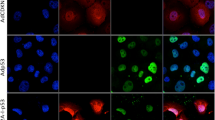
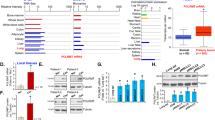
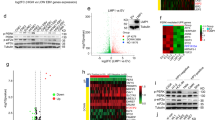
The p53 gene is the most frequently mutated gene in human cancers. Loss of functional p53 leads to impaired responses of cancer cells to apoptosis induction and to poor prognosis in patients with certain types of cancer. Cancer gene therapies using ectopic expression of wild-type p53 to force cancer cells through the apoptotic pathway have been tested extensively preclinically and clinically, and genes in various cell lines have been reported to be regulated upon ectopic p53 overexpression. However, the effect of p53 on many other p53-dependent and apoptosis-related genes remains unclear, as does the mechanism of p53-induced apoptosis in human cancers. In this study, we used real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction to evaluate the changes in expression of various p53-dependent and apoptosis-related genes in five human non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines with varying p53 statuses after adenoviral p53 treatment. We found that Ad/p53 induced the expression of the proapoptotic genes PUMA, Bak, Bax, and Fas in a cell type- and time-dependent manner. Among these genes, PUMA was upregulated the most dramatically and broadly. However, when a specific siRNA construct against PUMA was employed, we observed no attenuation of apoptosis in H1299 cells. Our data suggest that Ad-p53 induces the expression of a variety of proapoptotic genes and that lack of induction in one of these genes does not block Ad/p53-mediated cell killing in human lung cancer cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brugarolas J, Chandrasekaran C, Gordon JI, Beach D, Jacks T and Hannon GJ . (1995). Nature, 377, 552–557.
Caelles C, Helmberg A and Karin M . (1994). Nature, 370, 220–223.
Clayman GL, el Naggar AK, Lippman SM, Henderson YC, Frederick M, Merritt JA, Zumstein LA, Timmons TM, Liu TJ, Ginsberg L, Roth JA, Hong WK, Bruso P and Goepfert H . (1998). J. Clin. Oncol., 16, 2221–2232.
Deng C, Zhang P, Harper JW, Elledge SJ and Leder P . (1995). Cell, 82, 675–684.
el Deiry WS . (1998). Sem. Cancer Biol., 8, 345–357.
el Deiry WS, Kern SE, Pietenpol JA, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1992). Nat. Genes, 1, 45–49.
el Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1993). Cell, 75, 817–825.
Fields S and Jang SK . (1990). Science, 249, 1046–1049.
Friesen C, Herr I, Krammer PH and Debatin KM . (1996). Nat. Med., 2, 574–577.
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K and Elledge SJ . (1993). Cell, 75, 805–816.
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M . (1997). Nature, 387, 296–299.
Haupt Y, Rowan S, Shaulian E, Vousden KH and Oren M . (1995). Genes Dev., 9, 2170–2183.
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B and Harris CC . (1991). Science, 253, 49–53.
Kern SE, Kinzler KW, Bruskin A, Jarosz D, Friedman P, Prives C and Vogelstein B . (1991). Science, 252, 1708–1711.
Knudson CM, Tung KSK, Tourtellotte WG, Brown GAJ and Korsmeyer SJ . (1995). Science, 270, 96–99.
Kubbutat MH, Jones SN and Vousden KH . (1997). Nature, 387, 299–303.
Lane DP and Lain S . (2002). Trends Mol. Med., 8, S38–S42.
Levine AJ . (1997). Cell, 88, 323–331.
Lin Y, Ma W and Benchimol S . (2000). Nat. Genet., 26, 122–127.
Lindsten T, Ross AJ, King A, Zong WX, Rathmell JC, Shiels HA, Ulrich E, Waymire KG, Mahar P, Frauwirth K, Chen Y, Wei M, Eng VM, Adelman DM, Simon MC, Ma A, Golden JA, Evan G, Korsmeyer SJ, MacGregor GR and Thompson CB . (2000). Mol. Cell, 6, 1389–1399.
Mack DH, Vartikar J, Pipas JM and Laimins LA . (1993). Nature, 363, 281–283.
Miyashita T and Reed JC . (1995). Cell, 80, 293–299.
Nakano K and Vousden KH . (2001). Mol. Cell, 7, 683–694.
Nemunaitis J, Swisher SG, Timmons T, Connors D, Mack M, Doerksen L, Weill D, Wait J, Lawrence DD, Kemp BL, Fossella F, Glisson BS, Hong WK, Khuri FR, Kurie JM, Lee JJ, Lee JS, Nguyen DM, Nesbitt JC, Perez-Soler R, Pisters KM, Putnam JB, Richli WR, Shin DM and Walsh GL . (2000). J. Clin. Oncol., 18, 609–622.
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, Nemoto J, Shibue T, Yamashita T, Tokino T, Taniguchi T and Tanaka N . (2000a). Science, 288, 1053–1058.
Oda K, Arakawa H, Tanaka T, Matsuda K, Tanikawa C, Mori T, Nishimori H, Tamai K, Tokino T, Nakamura Y and Taya Y . (2000b). Cell, 102, 849–862.
Polyak K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (1997). Nature, 389, 300–305.
Quinlan DC, Davidson AG, Summers CL, Warden HE and Doshi HM . (1992). Cancer Res., 52, 4828–4831.
Reinke V and Lozano G . (1997). Oncogene, 15, 1527–1534.
Seto E, Usheva A, Zambetti GP, Momand J, Horikoshi N, Weinmann R, Levine AJ and Shenk T . (1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 89, 12028–12032.
Swisher SG, Roth JA, Nemunaitis J, Lawrence DD, Kemp BL, Carrasco CH, Connors DG, El-Naggar AK, Fossella F, Glisson BS, Hong WK, Khuri FR, Kurie JM, Lee JJ, Lee JS, Mack M, Merritt JA, Nguyen DM, Nesbitt JC, Perez-Soler R, Pisters KM, Putnam JBJ, Richli WR, Savin M and Waugh MK . (1999). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 91, 763–771.
Thor AD, Moore II DH, Edgerton SM, Kawasaki ES, Reihsaus E, Lynch HT, Marcus JN, Schwartz L, Chen LC and Mayall BH . (1992). J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 84, 845–855.
Vousden KH and Lu X . (2002). Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 594–604.
Wang L, Wu Q, Qiu P, Mirza A, McGuirk M, Kirschmeier P, Greene JR, Wang Y, Pickett CB and Liu S . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 43604–43610.
Xiang H, Kinoshita Y, Knudson CM, Korsmeyer SJ, Schwartzkroin PA and Morrison RS . (1998). J. Neurosci., 18, 1363–1373.
Yu J, Zhang L, Hwang PM, Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B . (2001). Mol. Cell, 7, 673–682.
Yu J, Wang Z, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B and Zhang L . (2003). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 100, 1931–1936.
Zhang WW, Fang X, Branch CD, Mazur W, French BA and Roth JA . (1993). Biotechniques, 15, 868–872.
Zhao R, Gish K, Murphy M, Yin Y, Notterman D, Hoffman WH, Tom E, Mack DH and Levine AJ . (2000). Genes Dev., 14, 981–993.
Acknowledgements
We thank Allan Prejusa and Henry Peng in the Keck Vector Core for adenovirus propagation and quality control, Gayle Nesom for editorial review and Alma Vega for assistance in preparing the manuscript. This work was supported in part by NCI grants (RO1 CA 092487-01A1 and RO1 CA 098582-01A1 to BF; PO1 CA78778-01A1 and Lung Cancer SPORE 2P50-CA70970-04 to JAR); an NIH Core Grant for Medium and Vectors (CA 16672); and a grant from the WM Keck Foundation. JG is an MD Anderson Odyssey Program Fellow supported by the Theodore N Law Endowment for Scientific Achievement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, J., Zhang, L., Swisher, S. et al. Induction of p53-regulated genes in lung cancer cells: implications of the mechanism for adenoviral p53-mediated apoptosis. Oncogene 23, 1300–1307 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207239
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207239
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Synthesis, and docking studies of novel heterocycles incorporating the indazolylthiazole moiety as antimicrobial and anticancer agents
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Multipolar mitosis of tetraploid cells: inhibition by p53 and dependency on Mos
The EMBO Journal (2010)
-
Mitochondrial control of cell death induced by hyperosmotic stress
Apoptosis (2007)
-
Inhibition of Bax activity is crucial for the antiapoptotic function of the human papillomavirus E6 oncoprotein
Oncogene (2006)